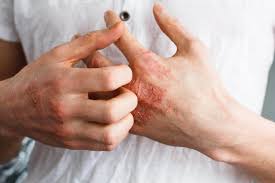
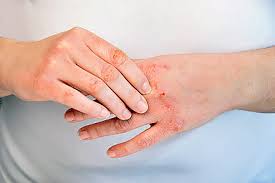
Eczema also known as **atopic dermatitis**, is a chronic skin condition that causes red, inflamed, itchy, and dry skin. It is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune-related factors. Eczema can affect various body parts, but one common and particularly challenging form is **hand eczema**, which affects the hands and fingers. Hand eczema can be especially difficult due to frequent exposure to irritants, water, and physical stressors, which can worsen symptoms.
Causes of Hand Eczema
Hand eczema often develops due to multiple factors, including:
1.Genetics: A family history of eczema or related conditions like asthma and hay fever increases the likelihood of developing eczema. Genetic mutations can disrupt the skin’s barrier function, making it more susceptible to irritation and dryness.
2.Irritants and Allergens: Frequent exposure to irritants like detergents, soap, water, chemicals, and dust can damage the skin barrier, triggering eczema. Allergic reactions to certain substances, like nickel in jewelry or fragrances in cosmetics, can also lead to hand eczema.
- Occupational Hazards: People in professions requiring frequent hand washing, such as healthcare workers, hairdressers, and cleaners, are at higher risk due to repeated exposure to irritants.
4.Immune System Response: Eczema is considered an immune-mediated condition, where the immune system overreacts to irritants, leading to inflammation, redness, and itching on the skin.
Symptoms of Hand Eczema
Redness and Swelling:Inflammation is indicate by common symptoms such as redness and swelling, which represent the body’s innate comeback to injury, infection, or irritation. The phenomenon of redness arises from an increase in blood move to the affected region, as blood vessels dilate, facilitating the delivery of iunsusceptible cells and essential nutrients to the site. Swelling, also well known as edema, occurs due to the accumulation of fluid as the body endeavors to safeguard and mend the harmed tissue. These symptoms often coexist with pain, heat, and impaired consequences in the affected region, particularly during episodes of severe inflammation.
Although these manifestations are generally temporary and indicative of the healing process, persistent or excessive redness and swelling may point to an underlying issue, such as an infection or a chronic inflammatory condition, which necessitates medical evaluation. Common treatment approaches include rest, the application of ice, elevation of the affected area, and the use of anti-inflammatory medications to alleviate discomfort and facilitate recovery.
Itching and Burning: Severe itching, burning, or stinging sensations are common and can worsen with scratching.
Dryness and Flaking: The skin often becomes dry, cracked, and scaly, which can be painful.
Blisters and Cracks: Some cases cause small, fluid-filled blisters that can burst and form painful cracks, especially in severe eczema cases.
Diagnosis and Types of Hand Eczema
Irritant Contact Dermatitis: Caused by frequent exposure to irritants like soaps and disinfectants, this is common in people whose jobs involve regular handwashing.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis: Triggered by an allergic reaction to substances like metals, fragrances, or latex.
Dyshidrotic Eczema: Characterized by small, itchy blisters on the sides of the fingers, palms, and sometimes soles of the feet.
A dermatologist typically diagnoses hand eczema based on a physical examination, patient history, and sometimes patch testing to identify specific allergens.
Treatment and Management of Hand Eczema
1.Moisturization: Using thick, fragrance-free creams or ointments helps restore the skin barrier, reduce dryness, and alleviate symptoms. Applying moisturizers after handwashing or exposure to water is recommended to lock in moisture.
2.Avoiding Irritants: Identifying and avoiding known triggers or irritants.Such as harsh soaps or gloves with certain materials, can prevent flare-ups.
3.Topical Medications: Corticosteroid creams or ointments are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and control symptoms. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory creams like calcineurin inhibitors are sometimes used to avoid steroid side effects for long-term use.
- Barrier Creams and Gloves: Using barrier creams and wearing gloves during tasks like cleaning. Dishwashing can help prevent contact with irritants.
5.Oral Medications: For severe or chronic cases, oral medications such as antihistamines (to reduce itching) . Immunosuppressants may be prescribed to control the immune response.
6.Phototherapy: In cases unresponsive to other treatments, phototherapy (light therapy) using ultraviolet light may reduce inflammation and improve skin appearance.
Prevention Tips for Hand Eczema
Limit Hand Washing:L Use lukewarm water and mild, fragrance-free soap, and avoid over-washing to prevent skin from drying out.
Wear Protective Gloves: Latex-free gloves can be worn while working with water, chemicals, or detergents to prevent irritation.
Choose Hypoallergenic Products: Opt for products without fragrances, dyes, or other potential irritants.
Moisturize Regularly: Applying a thick, unscented moisturizer after washing hands. Regular intervals during the day keeps the skin barrier intact.
Summary
Hand eczema is a challenging condition that requires consistent management and lifestyle adjustments. Avoiding irritants, using protective gloves, moisturizing regularly, and following medical treatment plans are key to controlling symptoms and reducing flare-ups. With proper care and attention, individuals can reduce the severity of hand eczema and improve the skin’s health and appearance.