Health and Safety ring a vast span of services and practices via keep and better real, mental, and social well-being. Here’s a breakdown of the key aspects:
Health
Health is a mood of utter real, mental, and social well-being, not only the leave of disease. It can be classified into different types:
(a) Physical Health
– It involves keeping a strong body, doing orderly, solid tasks, maintaining level nutrition, and avoiding harmful habits.
- Prevention to Management of malady: treat fast opinion, and use of diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
- Nutrition: A poise diet with carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
- Exercise: pretty in-task walking, running, strength training, and stretching to maintain fitness.
- Sleep: ample naps are key for the body’s repair and functioning.
(b) Mental Health
mentions inner, psychological, and social well-being.
- Common Issues: Anxiety, depression, bipolar mess, and schizophrenia.
- Mental Health Care: Therapy, counseling, and sometimes medications (like antidepressants or antipsychotics).
- Importance of Stress Management: Practising mindfulness, meditation, or other relaxation techniques.
(c) Social Health
- Center on your relationships with others and your role in the community.
- Good relationships, bear order, and social interactions contribute to overall well-being.
Care
keep refers to the services of individuals to maintain or improve their health. It includes:
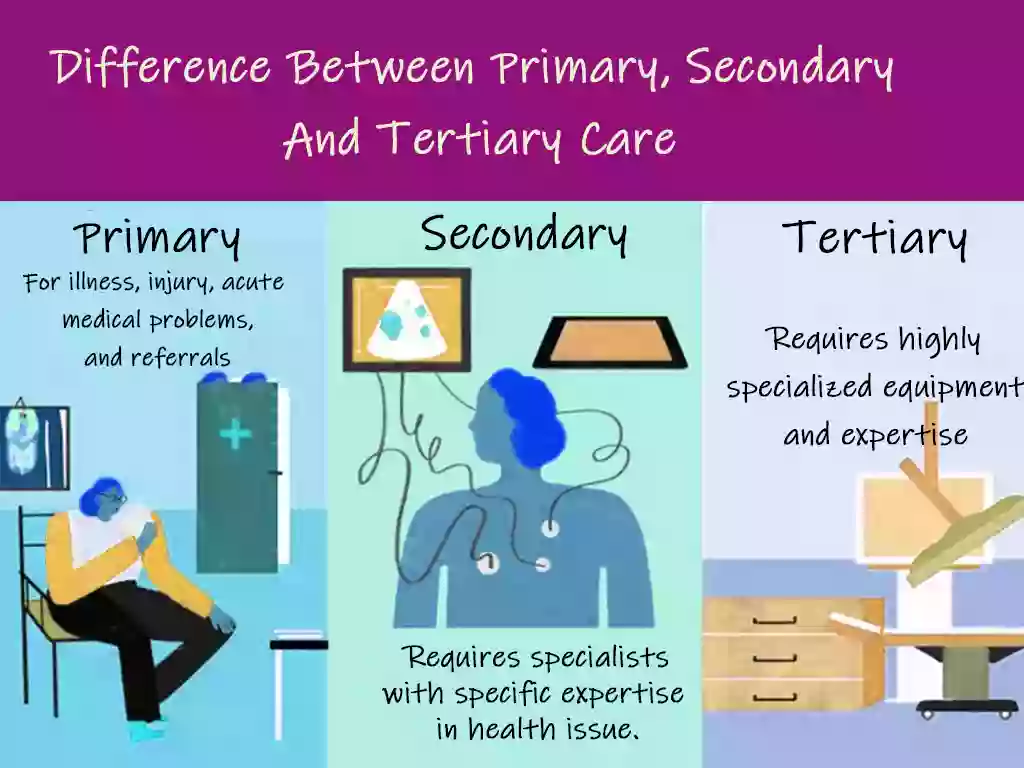
(a) Primary Care
The first contact point for health services is often provided by family doctors or general practitioners (GPs).
- Services Provided: Preventive care, vaccinations, screenings, management of chronic diseases, and acute illness treatment.
(b) Secondary Care
- Practice medical services provided by specialists like cardiologists, dermatologists, or endocrinologists.
- Patients are often referred by primary care providers for more detailed investigations or treatments.
(c) Tertiary Care
- Advanced, specialized care is provided in hospitals and medical centers. It includes surgery, chemotherapy, advanced diagnostics (like MRIs), and treatments for complex conditions.
(d) Quaternary Care
- Even more specialized care that is rare and complex, such as organ transplants, experimental treatments, or clinical trials.
Public Health
Public health focuses on preventing disease and promoting health at the population level:
- Vaccination Programs: Immunization to prevent infectious diseases like measles or flu.
- Health Education: Campaigns about healthy lifestyles, smoking cessation, safe sex, and hygiene.
- Environmental Health: Managing air and water quality, and preventing exposure to harmful chemicals.
Health And Safety Systems
Health systems vary globally and include organizations that provide health services:
- Universal Health Care (UHC): A system where healthcare is provided to all citizens regardless of their financial status.
- Private Health Care: Where services are provided by private entities, often funded by insurance or out-of-pocket payments.
- Public Health Care: Funded by the government, aiming to provide affordable services to the folk.
Health and Safety Professions
- Doctors/Physicians: cathartic professionals run for spotting and treating illnesses.
- Nurses: give day-to-day care, run drugs, and aid with calm control.
- Allied Health Professionals: cover real therapists, radiographers, dietitians, and work shrinks.
- Mental Health Professionals: Psychiatrists, psychologists, and counselors.
Health and Technology
Telemedicine: Online consultations between doctors and patients.
Health Apps: Mobile applications to track fitness, diet, medication, and mental well-being.
Wearable Devices: health tail that scanner heart rate, task volume, and sleep patterns.
Electronic Health Records (EHR): Digital records of patient’s health history, making data sharing easier across health providers.
Aging and Long-Term Care
- Old Care: aid and bear for older adults, plus tend homes, assisted living, and home care.
- Palliative Care: bear for those with serious illnesses, focusing on pain relief and quality of life.
- Hospice Care: End-of–life care that emphasizes comfort over curative treatments.
Challenges in Health and Care
- Access to Care: matters like long wait times, financial barriers, and geographic disparities.
- Health Inequalities: Disparities in health outcomes across different socioeconomic groups.
- Chronic Diseases: lead to long-term conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and mental illnesses.
- Workforce Shortages: Shortages of doctors, nurses, and healthcare professionals in many regions.
Preventive Health
- Lifestyle Changes: Encouraging healthy habits like a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco or excessive alcohol.
- Daily Screenings: Mammograms, colonoscopies, and blood pressure monitoring to detect diseases early.
This summary hand a broad overview of the unified areas of health and care, each crucial to overall well-being. Let me know if you need more detailed information on any specific topic.